VALVE PROSTHESIS
BIOLOGICAL VALVE PROSTHESIS
Most frequently implanted tissue valves are xenografts manufactured as bioprostheses, whereas allografts and autografts are being implanted less often
BIOPROSTHESIS
5. Medtronic–Mosaic 6. Medtronic–Mosaic Ultra
4. Sorin–Soprano Armonia 5. Edwards–Perimount Magna 6. Trifecga - SJM
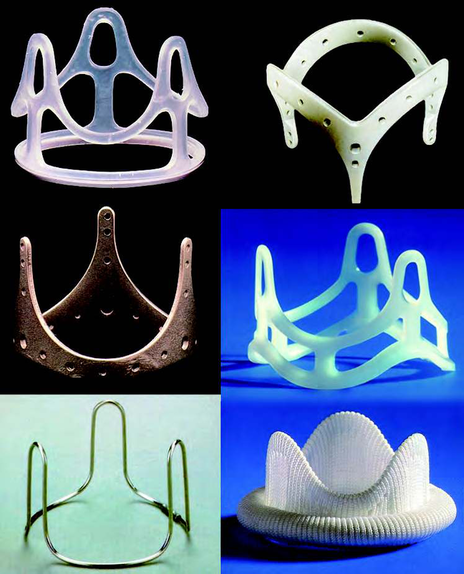
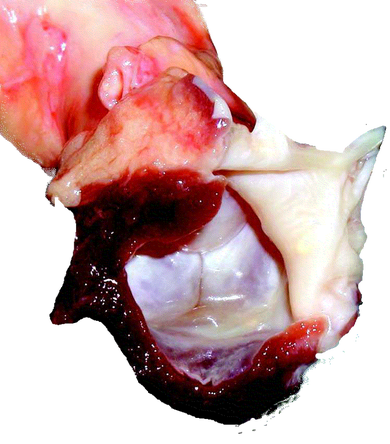
- Bioprostheses are xenografts that are mounted on a cloth-covered stent, which is manufactured from stellite, titanium, or plastic
- Its slight flexibility is desirable, as it helps to absorb stress load and thereby prolong the xenograft’s durability
- The stent is covered with Teflon or polypropylene and adapted for tissue-valve mounting
- The biological valve is either a porcine aortic valve or a valve assembled from bovine pericardium
- The most commonly used porcine valve bioprostheses include:
5. Medtronic–Mosaic 6. Medtronic–Mosaic Ultra
- The most commonly used bovine pericardium xenografts include:
4. Sorin–Soprano Armonia 5. Edwards–Perimount Magna 6. Trifecga - SJM
- The concept of detoxification (anticalcification, antidegenerative, antimineralization) treatment incorporated into the processing and storage of tissue valves
Stents for Bioprosthesis
Trifecta -SIM
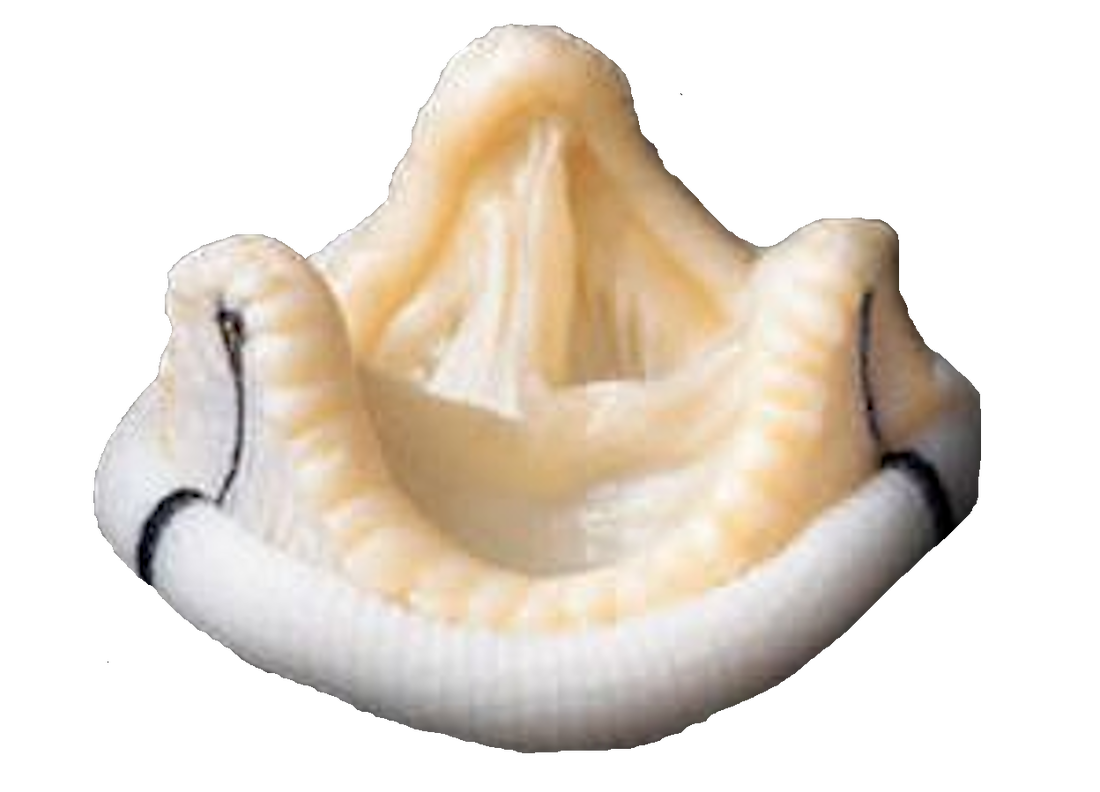
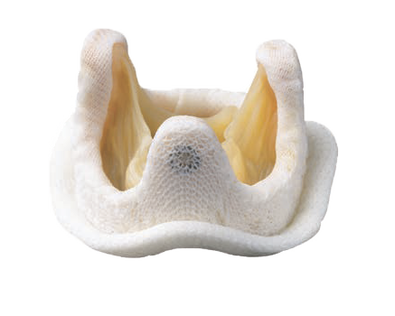
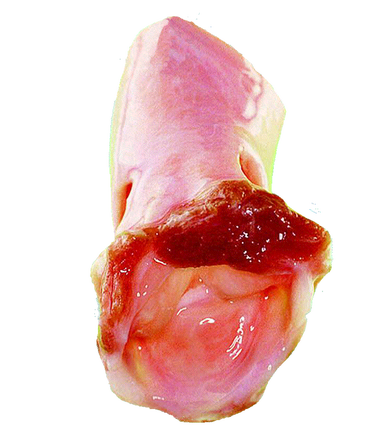
Stentless Bioprostheses
4. Sorin Freedom 5. Medtronic Freestyle 6. Elan, CryoLife-O’Brien
- Introduced by Tirone David in Toronto
- Have been implanted into the aortic position since 1988.
- They are xenografts, but they have neither stent nor sewing cuff
- Into a given patient’s aortic orifice, a stentless bioprosthesis that is larger than a stented one can be implanted (larger aortic EOA and lower transvalvular gradient)
- The best known stentless bioprostheses are :
4. Sorin Freedom 5. Medtronic Freestyle 6. Elan, CryoLife-O’Brien
- They have demonstrated superior hemodynamic features in terms of transvalvular gradients, EOA, and more complete regression of left ventricular hypertrophy
- However; the wave of enthusiasm in the mid- to late 1990s has waned because research data proved no superiority of stentless bioprostheses over stented ones in long-term studie
- Their implantation is technically more demanding and time-consuming.
- Bioprostheses designed for supraannular implantation where the sewing ring does not obstruct the aortic orifice area, and therefore the improved EOA is almost comparable to that of stentless bioprostheses
Allografts (Homografts)
- Allografts, human cadaverous aortic valves, are harvested usually in the course of multiorgan donor explantations, and are dissected as an aortic root with the valve and the ascending aorta
- Pulmonary allograft was discontinued due to use of aortic valve replacement, but it still has its place in paediatric cardiac surgery and also in the Ross procedure for replacement of the right ventricular outflow tract
- Explanted valve allografts are first treated with antibiotic solution and then frozen (cryopreservation, cryoconservation) and stored in liquid nitrogen at 190°C for up to 5 years
- After defrosting, the allografts’ tissue still contains viable fibroblasts.
- Endothelium is not preserved, which turns out to be beneficial for reducing the allograft antigenicity, and thereby no immunosuppression is needed after implantation
- In aortic position, their rate of degeneration is the same as with bioprostheses
- Do not contain any fabric and are less susceptible to infection than bioprostheses and mechanical valves; therefore, they are used mostly for aortic valve replacement for infective endocarditis
Autografts (Homografts)
- The pulmonary autograft is used for aortic valve replacement at the Ross procedure (and is itself, in its original place, substituted with a pulmonary allograft, replacing the right ventricular outflow tract with the pulmonary valve and the pulmonary trunk)
- The drawback of this procedure is its technical and time demands, as well as impending risk of failure of both implanted valves (autograft and allograft) in the long term