CORONARY ANATOMY
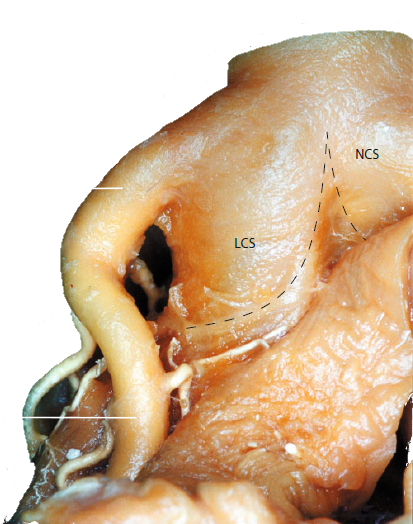
LEFT CORONARY ARTERY
LEFT CORONARY ARTERY
- Runs in the Left Coronary Groove (bordered anteriorly:pulmonary root and posteriorly: left atrium)
- Positioned just behind the posterior wall of the pulmonary root
2. The second segment: The Sternocostal Segment
- May be identified leaving the posterior wall of the pulmonary root
- still positioned in the left coronary groove
- May stretch between the pulmonary root and the anterior interventricular sulcus
- The length of this segment varies widely
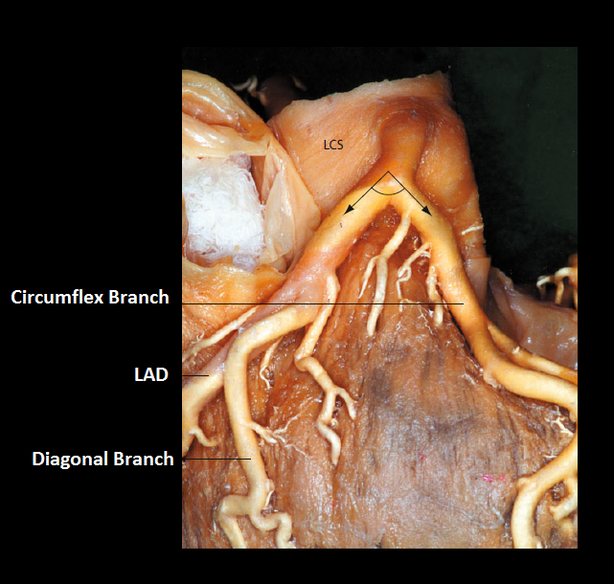
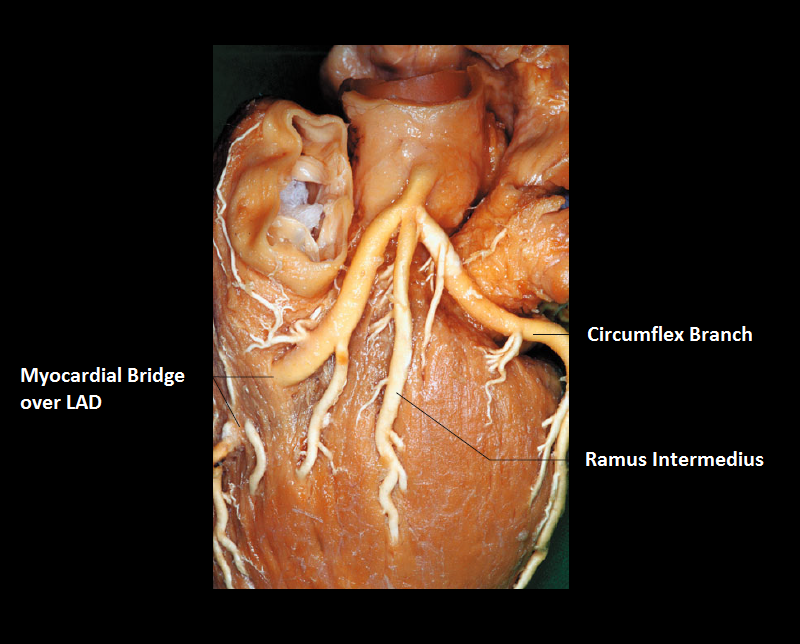
LONG LMS
- Blood supply area: sternocostal surface and left lateral surface of the heart
- Origin from the left coronary sinus
- Initial phase runs behind the pulmonary trunk in a forward direction
- According to its course, it can be divided into:
- Runs in the Left Coronary Groove (bordered anteriorly:pulmonary root and posteriorly: left atrium)
- Positioned just behind the posterior wall of the pulmonary root
2. The second segment: The Sternocostal Segment
- May be identified leaving the posterior wall of the pulmonary root
- still positioned in the left coronary groove
- May stretch between the pulmonary root and the anterior interventricular sulcus
- The length of this segment varies widely
LONG LMS
- Normally, the LMS branches just behind of the pulmonary trunk so that the sternocostal segment is absent.
- If it reaches the sternocostal surface of the heart and runs, without branching, into the left anterior descending artery (LAD) and the circumflex artery (Cx), into the anterior interventricular sulcus, it is called Long LMS.